ExtJS 4中的数据处理
ExtJS 4引入了新的Model类,并且对Store、Proxy等类进行了重大的重构,data包的重要类的组织形式如下图:
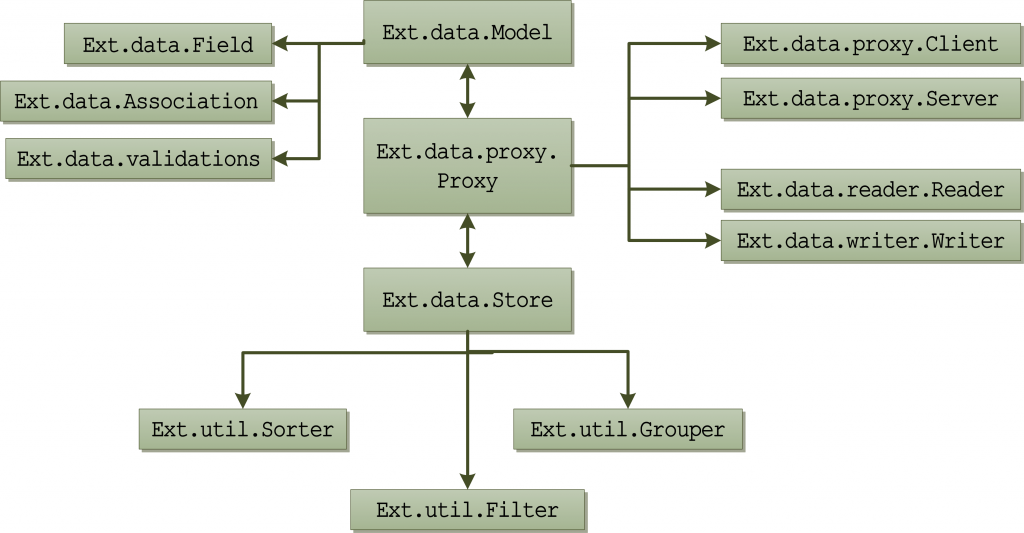
Model类是ExtJS 3的Record类的代替者,可以使用Model来表现真实世界中的实体对象,支持关联关系、数据验证、直接通过代理(不依赖Store)读取、保存数据,这些都是Record不支持的。Model类包含一系列表示实体属性的字段,以及若干用于操控实体数据的方法。
ExtJS 4不再支持Record类,但是,data包中某些类仍然在其方法名中包含“Record”字样。
模型的字段使用类Ext.data.Field表示,与ExtJS 3基本兼容,但是去除了allowBlank属性。
只需继承Ext.data.Model类,并声明模型支持的字段即可:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 |
Ext.define( 'Person', { extend : 'Ext.data.Model', fields : [ //每个字段均为Ext.data.Field的实例 { name : 'id', type : 'int' }, { name : 'name' //type字段用于指定字段的类型,类型主要用于数据格式的转换 //type可以使用字符串表示,也可以使用Ext.data.Types.*来表示 //如果不指定,默认类型是auto,表示不进行格式转换 }, { name : 'age', type : 'int' }, { name : 'birthday', type : 'date', dateFormat : 'd/m/Y' //遵守PHP日期格式规约 }, { name : 'alive', type : 'boolean', defaultValue : true //如果对象中没有指定该字段(undefined),则使用默认值,默认值默认为"" }, { name : 'weight', type : 'float' }, { name : 'weightKg', type : 'float', /*可以指定转换函数,用于把Reader读取到的值转换为Model字段*/ convert : function( value, record ) { var weightPounds = record.get( 'weight' ); //weight必须在前面声明 return Math.round( weightPounds * 0.45 ); } } ] } ); //等价的ExtJS 3声明 var Person = Ext.data.Record.create( [ { name : 'id', type : 'int' }, { name : 'name' }, { name : 'age', type : 'int' }, { name : 'birthday', type : 'date', dateFormat : 'd/m/Y' }, { name : 'alive', type : 'boolean', defaultValue : true }, { name : 'weight', type : 'float' }, { name : 'weightKg', type : 'float', convert : function( value, record ) { var weightPounds = record.get( 'weight' ); return Math.round( weightPounds * 0.45 ); } } ] ); |
ExtJS 4支持两种实例化模型的方式:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 |
//直接使用类实例化语法 var person = Ext.create( 'Person', { id : 10000, name : 'Jia Liang', age : 25, birthday : '05/26/1986', weight : 150 } ); //使用模型管理器创建 var person = Ext.ModelMgr.create( { id : 10000, name : 'Jia Liang', age : 25, birthday : '05/26/1986', weight : 150 }, 'Person' ); //获取模型实例的字段 var name = person.get( 'name' ); |
可以在模型类里面添加验证的声明:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 |
Ext.define( 'Person', { extend : 'Ext.data.Model', fields : [ { name : 'id', type : 'int' }, { name : 'name' }, { name : 'age', type : 'int' }, { name : 'birthday', type : 'date', dateFormat : 'd/m/Y' }, { name : 'alive', type : 'boolean', defaultValue : true }, { name : 'weight', type : 'float' } ], validations : [ { //要求目标字段必须存在,0被仍然是存在,空字符串被认为是不存在 type : 'presence', field : 'age' }, { //限定目标字段的长度在指定的范围内 type : 'length', field : 'name', min : 2, max : 60 }, { //限定目标字段匹配指定的正则式 type : 'format', field : 'name', matcher : /([a-z ]+)/ }, { //限定目标字段是列表里面的某个值 type : 'inclusion', field : 'gender', list : [ 'M', 'F' ] }, { //限定目标字段是是列表里面的任意值 type : 'exclusion', field : 'weight', list : [ 0 ] } ] } ); //执行验证 var errors = user.validate(); errors.isValid(); //是否验证成功 errors.items; //错误条目的列表:[{field:'name',message:'must be ...'} ,...] errors.getByField('name'); //获取指定字段的所有错误 |
在真实世界中,我们通常需要从服务器端获取实体数据,ExtJS 4的一个新特性是:可以在模型内部嵌入一个负责与服务器打交道的代理对象,我们可以脱离Store来进行数据的保存和加载:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 |
Ext.define( 'Person', { extend : 'Ext.data.Model', fields : [ { name : 'name' }, { name : 'age', type : 'int' }, { name : 'birthday', type : 'date', dateFormat : 'd/m/Y' }, { name : 'alive', type : 'boolean', defaultValue : true }, { name : 'weight', type : 'float' } ], //内嵌的代理对象 proxy : { type : 'rest', //使用RESTful风格的HTTP请求 url : '/sysmgr/personmgr/person', //纯名词的URL构成 reader : { type : 'json', root : 'object' } } } ); /* 通过发送GET请求到:/sysmgr/personmgr/person/10000来加载模型 * 如果proxy.format = 'json'则请求URL为/sysmgr/personmgr/person/10000.json * 服务器返回数据的格式: * { * success : true, * message : 'OK', * errorCode : '0', * object : { * id : 10000, * name : 'Jia Liang', * ...... * } * } * * */ Person.load( 10000, { success : function( person ) { console.log( "Loaded person: " + person.get( 'name' ) ); } } ); // 通过发送PUT请求到:/sysmgr/personmgr/person/10000来保存模型的更改 person.set( 'name', 'LiangJia' ); person.save( { success : function( person ) { console.log( "Updated person: " + person.get( 'name' ) ); } } ); //通过发送DELETE到:/sysmgr/personmgr/person/10000来执行模型的删除 person.destroy( { success : function() { console.log( "Destroyed person: " + person.get( 'name' ) ); } } ); //通过发送POST请求到:/sysmgr/personmgr/person来保存一个新的模型 //服务器应当返回带有id的持久化对象 var person = Ext.ModelMgr.create( { name : 'Alex Wang', age : 28 }, 'Person' ); person.save(); |
注意上面的例子,我们把proxy硬编码在Model类中了,如果想要在不同的proxy中加载模型,可以利用Store将Proxy与Model解耦:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 |
var store = Ext.create( 'Ext.data.Store', { model : 'Person', proxy : { type : 'rest', url : '/sysmgr/personmgr/person', format : 'json', reader : { type : 'json', root : 'object' } } } ); |
在ExtJS 4中,我们可以使用Ext.data.Association为实体指定关联,关联可以有两种形式:
- belongsTo:表示与其它实体的多对一(many-to-one)关联
- hasMany:表示与其它实体的一对多(one-to-many)关联
双向关联也是被ExtJS 4支持的。
下面是一个作者——书籍——章节的实体关联的例子:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 |
Ext.define( 'Author', { extend : 'Ext.data.Model', fields : [ { name : 'id', type : 'int' }, { name : 'name', type : 'string' } ], proxy : { type : 'rest', url : 'author', format : 'json', reader : { type : 'json', root : 'object' } }, //每个作者有多本书 hasMany : { model : 'Book', //目标实体:书 foreignKey : 'authorId' //目标实体引用当前实体标识符的字段,默认是author_id } } ); Ext.define( 'Book', { extend : 'Ext.data.Model', fields : [ { name : 'id', type : 'int' }, { name : 'title', type : 'string' }, { name : 'pages', type : 'int' }, { name : 'numChapters', type : 'int' }, { name : 'authorId', //这是一个外键字段 type : 'int' } ], proxy : { type : 'rest', url : 'book', format : 'json', reader : { type : 'json', root : 'object' } }, //每本书有多个章节 hasMany : { model : 'Chapter', //目标实体:章节 foreignKey : 'bookId' //目标实体引用当前实体标识符的字段 } } ); Ext.define( 'Chapter', { extend : 'Ext.data.Model', fields : [ { name : 'id', type : 'int' }, { name : 'number', type : 'int' }, { name : 'title', type : 'string' }, { name : 'bookId', //这是一个外键字段 type : 'int' } ], proxy : { type : 'rest', url : 'book', format : 'json', reader : { type : 'json', root : 'object' } } } ); |
对于hasMany属性,我们可以配置以下选项:
| 配置项 | 说明 |
| model | 关联目标模型的类名 |
| name | 在当前模型中创建的,代表获取关联实体的函数的名称,默认是目标实体的类名后面加s |
| primaryKey | 当前实体中作为主键使用的字段,默认id |
| foreignKey | 目标实体中作为外键使用的字段,默认为当前实体名后面加_id(全小写) |
| filterProperty | 用于覆盖目标实体默认的过滤器,如果没有设置,会自动根据foreignKey对目标实体进行过滤 |
下面是书籍与作者多对一关联的例子:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 |
Ext.define( 'Book', { extend : 'Ext.data.Model', fields : [ {name: 'authorId', type: 'int'} ], //一对多关联 hasMany : { model : 'Chapter', foreignKey : 'bookId' }, //多对一关联 belongsTo : { model : 'Author', foreignKey : 'authorId' //外键字段,本实体中引用目标实体主键的字段 } } ); |
对于hasMany属性,我们可以配置以下选项:
| 配置项 | 说明 |
| model | 关联目标模型的类名 |
| primaryKey | 目标实体中作为主键使用的字段,默认id |
| foreignKey | 当前实体中作为外键使用的字段,默认为目标实体名后面加_id(全小写) |
| getterName | 用于访问目标实体的getter的名称,默认为get目标实体名 |
| setterName | 用于访问目标实体的setter的名称,默认为set目标实体名 |
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 |
Ext.define( 'Book', { extend : 'Ext.data.Model', fields : [ ], associations : [ { type : 'hasMany', model : 'Chapter', foreignKey : 'bookId' }, { type : 'belongsTo', model : 'Author', foreignKey : 'authorId' } ] } ); |
如果配置了模型之间的关联关系,我们可以延迟的、按需的到服务器端加载数据,这与Hibernate的延迟加载有些类似:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 |
Author.load( 10000, { //自动到author/10000.json加载数据 success : function( author ) { //获取它的集合对象,其本质上是一个Ext.data.Store var books = author.books(); /** * 延迟加载:通过URL:book.json * 传递以下参数:其中filter是由关联关系确定的 * { * page : "1", * start : "0", * limit : "25", * filter : "[{'property':'authorId','value':10000}]" * } **/ books.load( { scope : this, callback : function( records, operation, success ) { console.log( records ); //读取:可以便利存储里面所有行 books.each( function( book ) { console.log( book ); } ); //写入:甚至我们可以在关联集合里面添加一个对象,并且同步到后端 books.add( { title : 'AutoTools Manual', pages : 250, numChapters : 7 } ); books.sync(); //对存储进行同步 } } ); } } ); Book.load( 10000100, { success : function( book ) { //读取:使用getter延迟加载关联的对象 //通过URL:author.json book.getAuthor( function( author ) { var name = author.get( 'name' ); } ); } } ); //注意,有多个回调函数可以配置 book.getAuthor( { callback : function( author, operation ) {}, //该回调总会被调用 success : function( author, operation ) {}, //处理成功时调用 failure : function( author, operation ) {}, //处理失败时调用 scope : this } ); //写入:调用setter会自动进行写入操作 book.setAuthor(1); book.set('authorId',1); //可以设置回调函数,在设置完毕后调用 book.setAuthor( 1, function( book, operation ) { console.log( book.get( 'authorId' ) ); } ); |
在ExtJS 4中,代理负责加载、保存数据。代理可以和Store或者直接和Model一起使用。在ExtJS 4中,代理可以分为两类:客户端代理、服务器代理,如下图:
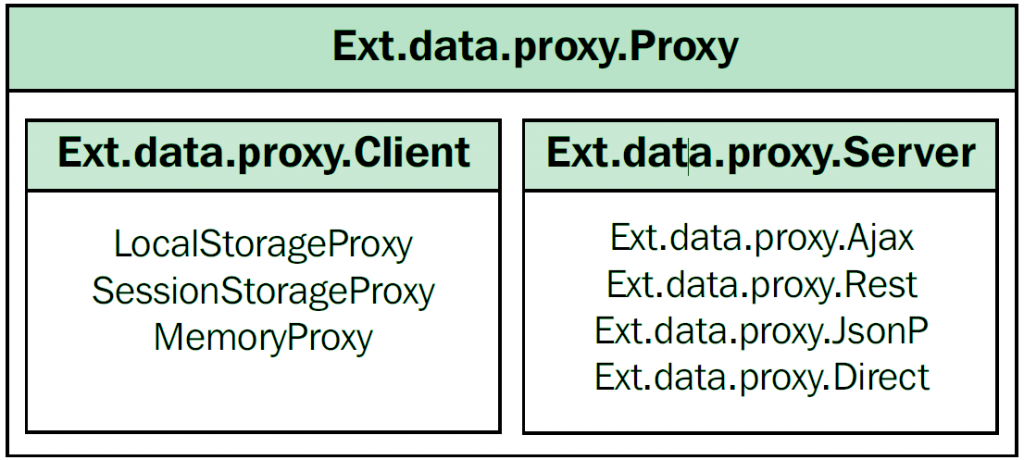
客户端代理使用浏览器的本地数据存储,本地数据存储是HTML5的重要特性,IE 8.0以上和其它现代浏览器均支持。
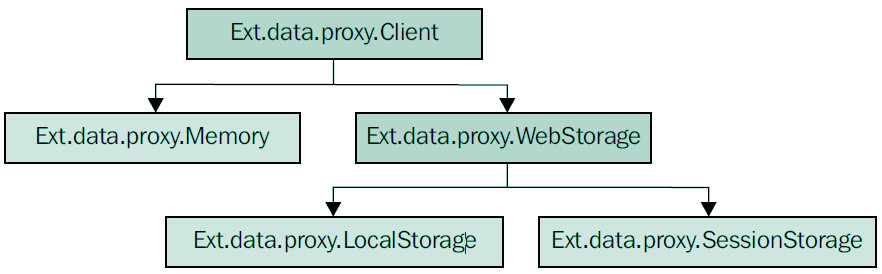
HTML5存储以键值对的形式存储数据,这些数据不像Cookie,后者会在某些时候发送给服务器。下图时客户端代理类层次:
下表是主要代理类的用法:
| 代理类 | 说明 | ||
| LocalStorageProxy | 使用HTML5本地存储(Local Storage)API来读写数据,这些数据是持久化的,即使关闭浏览器仍然存在。本地存储支持键值对的方式存储整数、字符串、布尔类型等,不过这些细节不需要关心,LocalStoreageProxy会负责把JavaScript串行化为字符串:
|
||
| SessionStorageProxy | 使用HTML会话存储(Session Storage),当会话结束(通常是关闭浏览器窗口),数据就会丢失:
|
||
| MemoryProxy | 在内存里边存取数据,一旦浏览器刷新,数据即丢失,下面是一个创建内存代理,并把数据提供给下拉框组件使用的例子:
|
服务器代理通过HTTP请求,从Web服务器加载或者保存数据。下面是服务器代理类层次图: 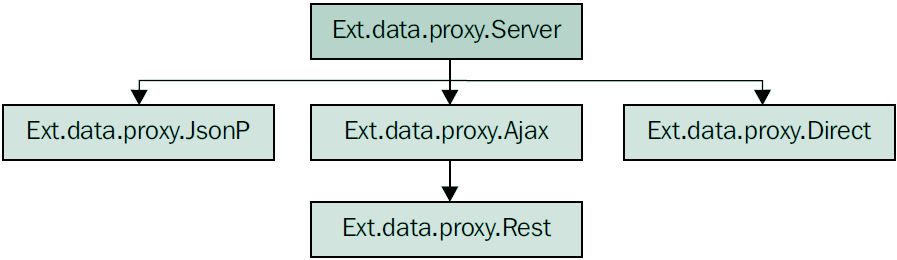
Ext.data.proxy.Server提供了一些公共的配置项,用于控制加载数据的方式:
| 配置项 | 说明 | ||
| api | 可以用来指定进行增删改查分别使用的URL,例如:
|
||
| batchActions | 在同步Store数据到Web服务器时,是否使用批量操作,默认true | ||
| batchOrder | 批量操作时增删改操作的顺序,使用逗号分隔,默认create,update,destroy | ||
| cacheString | 如果不使用缓存时,传递给Web服务器的时间戳参数,默认_dc | ||
| directionParam | 使用simpleSortMode时,用于指定排序方向的参数,默认dir | ||
| extraParams | 该参数用于指定额外的查询参数,每次请求发送时指定的冲突参数,将覆盖extraParams里面的值 | ||
| filterParam | 传递给Web服务器的filter参数,默认filter | ||
| groupDirectionParam | 使用simpleGroupMode时,用于指定分组的方向,默认groupDir | ||
| groupParam | 传递给Web服务器的group参数(用于指定分组列),默认group | ||
| startParam | 传递给Web服务器的start参数(用于限制数据开始索引),默认start | ||
| limitParam | 传递给Web服务器的limit参数(用于限制数据结束索引),默认limit | ||
| noCache | 是否通过添加时间戳参数来禁用缓存,默认true | ||
| pageParam | 传递给Web服务器的page参数(用于指定分页),默认page | ||
| simpleGroupMode | 如果为真,那么每次只允许发送单个group属性和单个group方向给后端 | ||
| simpleSortMode | 如果为真,那么每次只允许发送单个sort属性和单个sort方向给后端 | ||
| sortParam | 传递给Web服务器的sort参数(用于指定排序列),默认sort | ||
| timeout | 等待响应的超时毫秒数,默认30000,即30秒 | ||
| url | 用于请求数据的URL | ||
| model | 该代理关联的模型对象 | ||
| reader | 用于解析(Decoder)服务器数据的Ext.data.reader.Reader对象 | ||
| writer | 用于编码数(Encoder)据并发送给服务器的Ext.data.writer.Writer |
Ext.data.proxy.Server还提供了以下常用方法:
| 方法 | 说明 | ||
| read | 使用指定的Ext.data.Operation来进行读取操作 | ||
| create | 使用指定的Ext.data.Operation来进行创建操作 | ||
| destroy | 使用指定的Ext.data.Operation来进行销毁操作 | ||
| update | 使用指定的Ext.data.Operation来进行更新操作 | ||
| batch | 执行批量操作,Ext.data.Store的sync()方法内部即是调用该方法完成:
|
||
| setExtraParam | 设置“extraParams”属性的值 |
在调用上表的读写函数时,可以通过Ext.data.Operation来指定参数:
| 配置项 | 说明 |
| action | 该操作需要执行的动作类型,可以是 'create', 'read', 'update' 或者 'destroy' |
| batch | 指定该操作所属的Ext.data.Batch |
| filters | 过滤器的数组 |
| group | 分组配置 |
| limit | 希望从服务器加载的Model的数量 |
| sorters | 排序器的数组 |
| start | 分页时的起始偏移量 |
可以使用Ext.data.Operation来定义排序、过滤等规则:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 |
var operation = Ext.create( 'Ext.data.Operation', { action : 'read', start : 0, limit : 5 } ); //对应URL:/books?start=0&limit=5 proxy.read( operation ); //可以定制URL参数的名称 var operation = Ext.create( 'Ext.data.Operation', { action : 'read', startParam : 'firstRecord', limitParam : 'limitOfRecords', start : 0, limit : 5 } ); //对应URL:/books?firstRecord=0&limitOfRecords=5 proxy.read( operation ); //可以直接请求某一页的数据 var operation = Ext.create( 'Ext.data.Operation', { action : 'read', page : 5 } ); //对应URL:/books?page=5 proxy.read( operation ); //可以指定排序规则 var operation = Ext.create( 'Ext.data.Operation', { action : 'read', sorters : [ Ext.create( 'Ext.util.Sorter', { property : 'pages', direction : 'DESC' } ), Ext.create( 'Ext.util.Sorter', { property : 'numChapters', direction : 'DESC' } ), Ext.create( 'Ext.util.Sorter', { property : 'title', direction : 'ASC' } ) ] } ); //对应URL:/books?sort=[{"property":"pages","direction":"DESC"},{"property":"numChapters","direction":"DESC"},{"property":"title","direction":"ASC"}] proxy.read( operation ); //指定过滤器时类似 var operation = Ext.create( 'Ext.data.Operation', { action : 'read', filters : [ Ext.create( 'Ext.util.Filter', { property : 'pages', value : '250' } ) ] } ); //对应URL:/books?filter=[{"property":"pages","value":"250"}] proxy.read( operation ); //甚至,可以自己定义如何把过滤器、排序器进行编码,以适配服务器支持的模式 var proxy = Ext.create( 'Ext.data.proxy.Ajax', { url : '/books', model : 'Book', encodeSorters : function( sorters ) { var length = sorters.length; var sortStrs = []; var sorter, i; for ( i = 0; i < length; i++ ) { sorter = sorters[i]; sortStrs[i] = sorter.property + ',' + sorter.direction; } return sortStrs.join( ";" ); }, encodeFilters : function( filters ) { var length = filters.length; var filterStrs = []; var filter, i; for ( i = 0; i < length; i++ ) { filter = filters[i]; filterStrs[i] = filter.property + ',' + filter.value; } return filterStrs.join( ";" ); } } ); //对应URL:/books?start=0&limit=5&sort=pages,DESC;numChapters,DESC;title,ASC&filter:pages,250 proxy.read( operation ); |
下表列出主要的服务器代理类及其用法说明:
| 代理类 | 说明 | ||||||
| Ajax |
这是最常使用的代理,使用普通的Ajax请求来加载、存储数据到Web服务器,在ExtJS 3中,它对应了Ext.data.HttpProxy。只需要指定type为ajax即可,下面是一个简单的例子:
当代理发起读请求时,会使用GET方式;当发起写请求(增删改)时,会使用POST请求。必须使用api配置项为CURD分别指定URL。 Ajax代理只能用于访问当前域(domain)的URL。 |
||||||
| Rest | 这是AjaxProxy的子类型,使用不同的HTTP方法来表示CRUD操作,不需要分别指定URL。 | ||||||
| JsonP | 用于跨站请求数据,对应ExtJS 3的Ext.data.ScriptTagProxy。其本质上是在HTML中嵌入一个URL为跨域脚本的<script>元素,效果如下:
要使用JsonP代理,可以使用类似下面的代码:
在进行数据读写时,不需要关注内部细节,JsonP代理会处理好。 对于跨站Web服务,必须处理好回调,示例如下:
|
Store主要用于作为Model的容器(管理Model的集合),并且可以配置一个Proxy用于加载/保存数据。同时,Store还负责排序、过滤、分组,下图是Store的类层次图:
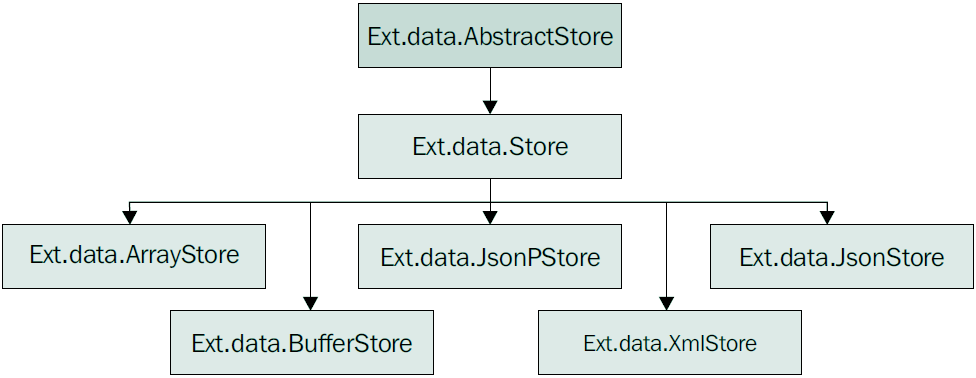
其中ArrayStore用于直接读取数组对象:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 |
var blogData = [ [ 1, 'http://loianegroner.com' ], [ 2, 'http://loiane.com' ] ]; var store = Ext.create( 'Ext.data.ArrayStore', { model : 'Blog', data : blogData //直接使用内存中的数组 } ); store.load( function( records ) { var blog, i; for ( i = 0; i < records.length; i++ ) { blog = records[i].data; } } ); |
Reader用于解码来自来自服务器,加载到Model实例或者Store的原始数据。在ExtJS 3中,Reader被耦合到Store中,而在ExtJS 4则耦合到Proxy中。Reader的类层次结构如下:
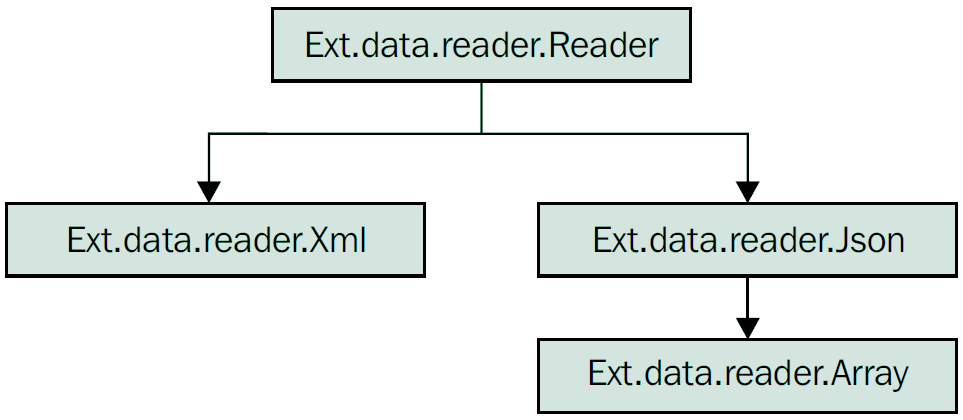
Ext.data.reader.Reader包含以下常用的配置项:
| 配置项 | 说明 |
| idProperty | 模型的标识符属性从什么字段读取,默认与模型的id字段一致 |
| messageProperty | 包含响应消息的字段 |
| croot | 包含模型列表的字段 |
| successProperty | 包含是否成功的字段,默认为success |
| totalProperty | 包含数据集总数的字段,默认为total,在分页时使用 |
对于Ext.data.reader.Json,服务器端的响应数据必须匹配如下格式(而不能单单发送Model的数组):
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 |
//模板: { "successProperty" : true, "messageProperty" : 'Message from server', "totalProperty",100, "croot" : [{},{}] } //实例: { "success" : true, "message" : 'Operation OK', "tota",100, "object" : [{userId:1,name:'Alex'},{userId:2,name:'Meng'}] } |
Writer负责编码JavaScript数据为服务识别的形式,类层次如下:
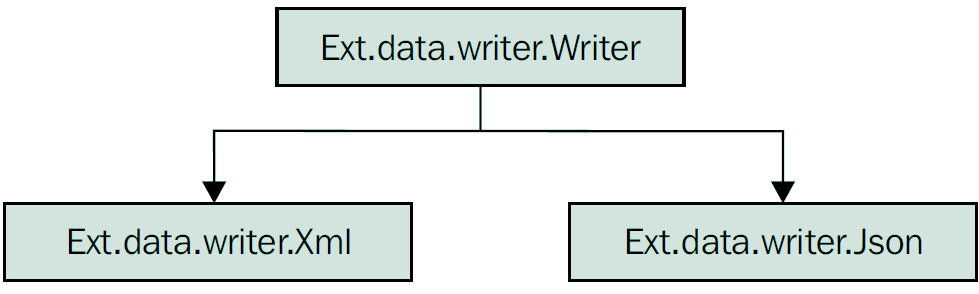
Writer包含配置项:
| 配置项 | 说明 |
| nameProperty | 需要作为发送给后台字段名的Model属性,默认name |
| writeAllFields | 是否发送所有字段到服务器,如果为false,则只发送被修改的字段,默认true |
下面是JsonWriter的使用例子:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 |
var store = Ext.create( 'Ext.data.Store', { model : 'Blog', proxy : { type : 'ajax', api : { read : 'data/blogs/read', create : 'data/blogs/create', update : 'data/blogs/update', destroy : 'data/blogs/delete' }, reader : { type : 'json', root : 'blogs' }, writer : { type : 'json', writeAllFields : false, root : 'data' } } } ); //添加一条记录 var blog = Ext.ModelManager.create( { url : 'http://gmem.cc' }, 'Blog' ); store.insert( 0, blog ); //代理将发送一条POST请求到data/blogs/create //内容:{"data":{"id":"","url":"http://gmem.cc"}} blog.setUrl('http://gmem.net'); //代理将发送一条POST请求到data/blogs/update //内容:{"data":{"id":"100","url":"http://gmem.net"}} store.remove(blog); //代理将发送一条POST请求到data/blogs/delete //内容:{"data":{"id":"100","url":"http://gmem.net"}} |
在ExtJS 4中,Store负责排序,排序规则由sorters配置项决定,浏览器端排序(Local)、服务器端排序(Remote)均被支持。每个排序对象均为Ext.util.Sorter的实例。
下面是客户端排序、服务器端排序的例子:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 |
Ext.define( 'Book', { extend : 'Ext.data.Model', fields : [ {name: 'id', type: 'int'}, {name: 'title', type: 'string'}, {name: 'pages', type: 'int'}, {name: 'numChapters', type: 'int'}, {name: 'subject', type: 'string'} ], proxy : { type : 'ajax', url : 'data/books/books.json' } } ); var store = Ext.create( 'Ext.data.Store', { model : 'Book', //声明排序器:以页数为主要排序降序排列,以章节数为第二排序升序排列 sorters : [ { property : 'pages', direction : 'DESC' }, { property : 'numChapters', direction : 'ASC' } ] } ); store.load();//自动依据sorters的设置来进行客户端排序 store.sort('subject','ASC'); //使用sort函数,可以随时执行排序 //要进行服务器端排序,只需要指定remoteSort为true: var store = Ext.create( 'Ext.data.Store', { remotSort : true } ); //自动把排序请求发送给服务器处理: //sort:[{"property":"pages","direction":"DESC"},{"property":"numChapters","direction":"ASC"}] store.load(); |
与排序非常类似,ExtJS 4支持浏览器端排序(Local)、服务器端排序(Remote)的数据过滤,每个过滤器对象是Ext.util.Filter的实例。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 |
var store = Ext.create( 'Ext.data.Store', { model : 'Book', filters : [ { property : 'subject', value : 'JAVA' }, { property : 'numChapters', value : '13' } ] } ); //进行客户端过滤 store.filter( 'numChapters', 10 ); //如果要进行服务器端过滤,只需要设置remoteFilter为true var store = Ext.create( 'Ext.data.Store', { remoteFilter : true } ); //加载数据时,自动把过滤器编码并发送给服务器 //filter:[{"property":"subject","value":"JAVA"},{"property":"numChapters","value":13}] store.load(); |

Leave a Reply