Blender知识集锦
| 快捷键 | 说明 |
| 右键 | 单选元素 |
| Shift 右键 | 追加元素(物体、点、线或者面)到选区 |
| Ctrl I | 反选元素 |
| A | 全选/全不选 |
| B 左键 | 以矩形框追加元素到选区 |
| C 中键 | 以笔刷修剪选区 滚动鼠标滚轮,可以修改笔刷大小 |
| Ctrl 左键拖动 | 以套索追加元素到选区 |
| Ctrl 左键点击 | 以当前选中的元素为基准,快速添加新的元素 |
| Ctrl Shift 左键 | 以套索修剪选区 |
| Alt 右键 |
选取一圈子的面,按住Alt,点击右键选取一个面,再次点击右键选取一个面,顺着这两个面方向的一圈子面都被选中 选取边的时候,按Alt 右键,选择循环边;按Ctrl Alt 右键,选择平行边 |
| Ctrl 右键 |
选取一个范围的面,按住Ctrl,点击右键选取一个面,再次点击右键选取一个面,则两个面之间的所有面都被选中 该快捷键可以和Shift 右键联合使用 |
| Ctrl 小键盘 + / - | 选择更多/更少:首先选择一个元素,然后按此快捷键,可以选择周围的元素 |
| Ctrl Shift 小键盘 + / - | 选择更多/更少:首先选择两个元素E1、E2,然后按此快捷键,可以继续选择下一个元素E3,使得E3与E2的位置关系、E2与E1的位置关系相同 |
| Ctrl Tab | 子模式切换:在编辑模式(Edit Mode)下,切换选取的目标:点、线、面 |
| Ctrl + | 增加选区 |
| Ctrl - | 缩小选区 |
| L |
鼠标悬停在元素上,按L可以选中所有与之关联(属于同一物体)的元素 点选元素后,按Ctrl L也可以 |
| 中键 | 旋转视图 |
| Shift 中键 | 平移视图 |
| Ctrl 中键 | 缩放视图,或者中键滚轮也可以 |
| 小键盘0 | 进入/退出摄像机视角 |
| Ctrl + 小键盘0 | 进入/退出活动摄像机视角 |
| 小键盘5 | 透视/正交视角切换 |
| 小键盘1 | 从正前方观察。Ctrl 小键盘1则从正后方 |
| 小键盘3 | 从正右方观察。Ctrl 小键盘3则从正左方 |
| 小键盘7 | 从正上方观察。Ctrl 小键盘7则从正下方 |
| Ctrl Alt Q | 切换上/前/右/透视四画面 |
| Home | 显示所有物体 |
| 小键盘. | 放大、居中显示选中物体 |
| 小键盘/ | 放大、居中显示选中物体,并且隔离其它未选中物体 |
| 左键 | 移动3D游标 |
| Shift C | 重置视图,3D游标回到原点 |
| Z | 切换以线框/实体(纯色)来显示物体 |
| Alt Z | 切换以纹理/实体(纯色)来显示物体 |
| Shift Z | 切换以渲染结果/实体(纯色)来显示物体 |
| Ctrl R |
编辑模式下,悬停在两条平行线框之间:
可以用于曲线的细分 |
| K | 切割 |
| Y | 分离选中的面,后续用右键移动被分离的面 |
| E | 抬升。Alt E 调出选项菜单 |
| Ctrl B | 选中一个元素,制造倒角。移动鼠标改变倒角高度,滚动滚轮增加分段数 |
| V | 撕开选中的边 |
| Alt V | 撕开选中的边并填充,注意3D游标的位置 |
| F | 选中两个顶点,然后连接为线,或者选中三个以上顶点,连接为面 |
| P | 将选区独立为新的物体 |
| G G | 滑移:受限制的移动线或面 |
| X | 删除元素 |
| I |
在选中的面上新增一个内插的面:
|
| W | 特殊菜单项,细分、平滑等功能在此 |
| Ctrl V / E / F | 编辑模式下与点、线、面有关的命令 |
| M | 放置元素到层 |
| Shift R | 重复上一次动作,例如上一次动作为细分,则按此快捷键可进一步细分 |
| Alt S | 法向缩放 |
| Alt R | 旋绕(Spin)工具 |
| Alt D | 在点选择模式下,添加新的点 |
| U | UV映射 |
| Shift H | 隐藏未选择部分 |
| Alt H | 显示隐藏部分 |
| 物体模式下的快捷键 | |
| Shift A | 添加物体 |
| G |
移动物体。GZ仅仅在Z轴方向移动,GY、GX类似。G5移动5 G后,按Shift X,表示在Y、Z方向移动(排除X方向) |
| S |
缩放物体。SZ仅仅在Z轴方向缩放,SY、SX类似。S2放大二倍 SX0,可以多个面的法线一律平行于X轴 |
| R | 旋转物体。RZ仅仅在Z轴方向旋转,RY、RX类似 |
| Ctrl Alt Shift C | 设置物体的质心(Origin) |
| Shift D | 复制物体 |
| Alt D | 复制链接(Linked)物体 |
| Shift S |
吸附(Snap)操作,例如:
|
| Ctrl J | 把多个物体合并为一个 |
| Ctrl G | 物体分组 |
| Shift G | 选择物体所在的分组 |
| Ctrl A | 应用。具有重置位置、缩放、旋转值的作用,N面板中的数值会重置 |
| Alt C | 将曲线、文本、表面转换未Mesh,或者反向转换 |
| O | 比例化编辑 |
| 动画快捷键 | |
| Alt A | 播放/暂停 |
| Shift Alt A | 倒放的播放/暂停 |
| Left Right | 前进或者后退一帧 |
| Shift Left Shfit Right |
转到时间线开始/结束处 |
| Shift Up Shift Down |
跳跃10帧 |
| Blender界面快捷键 | |
| T | 显示/关闭左侧面板 |
| N | 显示/关闭右侧面板 |
| A | 鼠标悬停,可以展开/折叠面板中的字段集 |
| Shift + Space | 扩大编辑器面板 |
| 圆盘菜单快捷键 | |
| Tab | 切换物体交互模式 |
| Z | 切换物体渲染方式 |
| Q | 切换查看角度 |
| . | 切换旋转、缩放时使用的轴心点(Pivot Point) |
| Ctrl Shift Tab | 切换吸附(Snap)点 |
N打开面板,在Display控件中,把Lines设置为0
左键按住其源面板由上角的grabber(小三角),稍微拖动一下即可。
按O键启用。其效果是:以选中的元素为基准,按照特定的衰减函数,对物体进行整体变换。离选中元素越近的元素,受变换的影响越大。选择的轴心点也会影响到变换的效果
操作步骤:
- 以边选择模式,选中一个边,按Ctrl B执行倒角
- 移动鼠标,可以修改倒角面的大小
- 滚动滚轮,可以对倒角面进行细分,产生圆角效果
- 按F6,可以设置属性,Profile用于控制形成凸面还是凹面(曲率)
注意:F6的设置会被记住,下一次倒角其参数被自动使用
即Tools面板中Transform字段集中的Shrink/Fatten功能,快捷键Alt S。所谓法向缩放,就是让各面分别沿着其法线的方向进行放大或者缩小,在设计建筑时可以用到。操作步骤:
- Alt 右键,选取需要缩放的循环面
- 按E挤出,立即回车,不进行实质上的挤出操作
- Alt S激活法向缩放,在缩放期间,可以按S启用Even Thickness
顶部的凸台就是利用法线缩放生成的。
选中多个面并进行挤出时,可以按Alt E调出选项:
- Region,默认的挤出方式,所有面统一方向
- Individual faces,各面沿着自己的法线方向挤出
注意:E键挤出后,用右键取消,实际上相当于0距离挤出,也就是新的面已经存在。要取消,应该通过Ctrl Z。
即Tools面板Add字段集中的Spin按钮,快捷键Alt R。一般在编辑模式的正交视图下、侧面进行操作。可以让目标Mesh以3D游标为中心,旋转一定的角度。下图是平面绕旋转100度的效果示意:

即Tools面板Add字段集中的刀片(切割)、Select(选择)按钮,快捷键分别为K、Shift K。
刀片工具,用于在Mesh表面切分出更多的面出来,操作完毕后,按Enter确认。
选择工具,要求首先选择一系列的面,然后Shift K绘制一个路径(直线),Enter确认。路径经过的地方,会被切分出新的面。
即Tools面板Add字段中的切割(Bisect)按钮,可以用一个平面来割掉Mesh的一部分。操作步骤:
- 进入编辑模式,按A全选目标Mesh
- 点击Bisect按钮,单击一点作为平面起点,然后拖拽,到终点处再次单击,定义一个切割平面
- 按F6,Fill表示是否对截面进行填充,Clear Inner/Outer指示切除平面内侧还是外侧的哪一部分
可以在编辑模式下,根据两个几何图像的并、交、差集,确定Mesh的最终形态。例如,用立方体对球体进行打洞的例子:
- 创建一个UV球,进入编辑模式,取消选择
- 创建一个Cube,缩放,使其穿过球体。此时Cube处于选中状态
- 按Ctrl F,选择Intersect(Boolean),按F6
- Boolean取值Difference,表示保留未选中元素中、不属于选中元素的部分,即打洞
- Boolean取值Intersect,表示保留两者共同的部分
- Boolean取值Union,表示保留两者的并集
可以连接多个游离平面的循环边,创建多个面。操作步骤:
- 在编辑模式下,为一个Mesh创建多个游离的平面
- 选中所有平面,按快捷键W,选择Bridge Edge Loops,按F6
- Connect Loops,可以选择开放/闭合最后一个、第一个面
- Number of Cuts,对创建的新面进行细分
注意游离平面的顺序、旋转角度很重要。桥接也可以用于其它二维几何图形。
LoopTools的Bridge也可以实现类似的功能。
选中若干面,按Ctrl F,选择Solidify,然后F6,可以增加厚度(立体化)。
编辑模式,点击![]() 启用吸附,右侧Snap Element选择顶点。在你移动顶点时,会自动吸附到临近的顶点,合而为一。
启用吸附,右侧Snap Element选择顶点。在你移动顶点时,会自动吸附到临近的顶点,合而为一。
- 添加Curve ⇨ Path,进入编辑模式。选中一个点,按E可以凸起
- 右侧曲线面板,设置Active Spline的Order为2可以绘制直角管道
- 右侧曲线面板,设置Shape为3D,Fill为Full。Bevel的Depth、Resolution可以用来绘制圆管
- 完毕后,Alt + C转换为Mesh
使用此插件,可以方便制作拓扑曲面。
操作步骤:
- 作为参考的物体,可以在右侧大纲中,点击
 ,禁止在Viewport中选中
,禁止在Viewport中选中 - 添加一个Mesh,例如平面,进入编辑模式,删除其所有顶点。即将制作的曲面将以此Mesh为容器
- 左侧选择GP面板(Grease Pencil),Data Source选择Object,Stroke Placement选择Surface。表示手绘线体置于参考物体表面
- 按住D,在参考物体表面绘制线条,切换视角你会注意到,线条沿着物体表面延伸
- 左侧选择Tools面板,找到Bsurfaces一段,点击Add Surface,F6修改参数
- 工具栏点击
 ,其后的下拉框选择
,其后的下拉框选择 ,点选
,点选 。这些设置表示转换(移动/缩放/旋转)时吸附到参考物体表面
。这些设置表示转换(移动/缩放/旋转)时吸附到参考物体表面 - A全选所有元素,按一下G,不做任何变动,G仅仅是触发一下转换
类似的,你可以在执行上节第6步的情况下,转换细分过的平面,让它吸附到参考物体的表面。
该插件需要启用,在编辑模式下,按W键可以看到LoopTools的菜单项
可以连接两对游离的循环边,生成新的面。功能类似于Bridge Edge Loops。
可以让选中的面几何的外边缘圆化。
选取几个采样点,基于这些点曲线化一系列相邻的边。 示例:
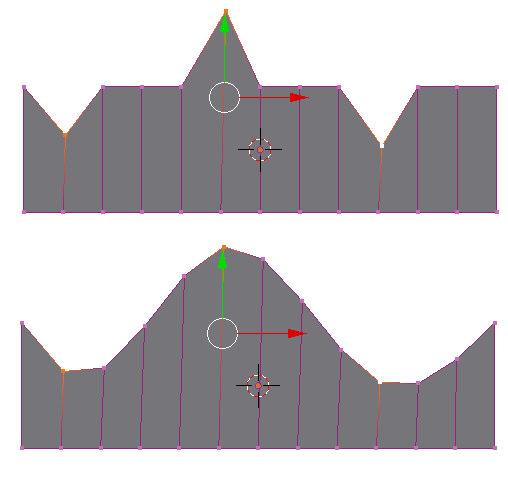
图中上半部分,呈现为桔黄色的三个点,被选中作为采样点。然后按W键选择Loop Tools ⇨ Curve,即可得到下半部分的效果。
具有平缓曲线的效果,以上图下半部分为例,选中曲线上的所有点,然后W键选择Loop Tools ⇨ Relax,Shift R重复,即可逐步的让曲线平缓。
吸附倒GP线:使用蜡笔绘制一条曲线,然后选中曲线上所有点,自动连接曲线点、蜡笔Mesh化后的点,形成多个面。
放样,可以把两个或者是多个二维曲线符合成三维物体。比如下面这个效果是利用3个在Z方向圆心重合的Circle进行Loft得到的:

等距:可以让一条曲线上的点分布的更加均匀。
简单操作步骤:
- 进入编辑模式
- 按U键,打开UV映射菜单
- Unwrap,直接展开,基于缝合边设定进行展开
- Smart UV project,智能UV映射
- 选择智能UV映射,F6打开属性菜单
- Island Margin,孤岛边距,可以设置各个展开面的边距。避免“贴图出血”
- 切换到边选择模式
- 选定缝合边,所谓缝合边,是指从它们裁剪开物体的边
- Ctrl + E,标记缝合边(Mark Seam)
- A全选,U选择Unwrap
盒子十字展开技巧:侧面四个边、顶面3个边作为缝合边。
圆柱展开技巧:上下底,外加任意一条竖边作为缝合边。通常选择正交视图的前/侧视图的正前方的那个边
点击按钮![]() ,则编辑模式下,选区和UV保持同步
,则编辑模式下,选区和UV保持同步
在面选择模式下,Ctrl + L可以选择同一UV孤岛中的所有面。做复杂UV展开时可以Shift + H 隐藏未选择部分 。




Leave a Reply