Dubbo知识集锦
节选自:https://dubbo.apache.org/zh-cn/blog/rpc-introduction.html,稍作改动。
RPC(Remote Procedure Call)即远程过程调用,它是一种通过网络从远程计算机程序上请求服务,而不需要了解底层网络技术的协议。也就是说两台服务器A,B,一个应用部署在A服务器上,想要调用B服务器上应用提供的方法,由于不在一个内存空间,不能直接调用,需要通过网络来表达调用的语义和传达调用的数据。
RPC协议假定某些传输协议的存在,如TCP或UDP,为通信程序之间携带信息数据。在OSI网络通信模型中,RPC跨越了传输层和应用层。RPC使得开发包括网络分布式多程序在内的应用程序更加容易。现在业界有很多开源的优秀 RPC 框架,例如 Spring Cloud、Dubbo、Thrift 等。
RPC 这个概念术语在上世纪 80 年代由 Bruce Jay Nelson 提出。在 Nelson 的论文 "Implementing Remote Procedure Calls" 中提到了RPC的几点优势:
- 简单:RPC 概念的语义十分清晰和简单,这样建立分布式计算就更容易
- 高效:过程调用看起来十分简单而且高效
- 通用:在单机计算中过程往往是不同算法部分间最重要的通信机制
通俗一点说,就是一般程序员对于本地的过程调用很熟悉,那么我们把 RPC 作成和本地调用完全类似,那么就更容易被接受,使用起来毫无障碍。Nelson 的论文发表于 30 年前,其观点今天看来确实高瞻远瞩,今天我们使用的 RPC 框架基本就是按这个目标来实现的。
Nelson 的论文中的RPC包含以下角色:
- User(客户端):像调用本地服务似的调用远程服务
- User-stub:接收到调用后,将方法、参数序列化;接收到结果消息,并进行解码(将结果消息反序列化)
- RPCRuntime
- Server-stub:收到消息后进行解码(将消息对象反序列化)、根据解码结果调用本地的服务、将返回结果打包成消息(将结果消息对象序列化)
- Server(服务器)实现服务逻辑
它们之间的交互流程如下:
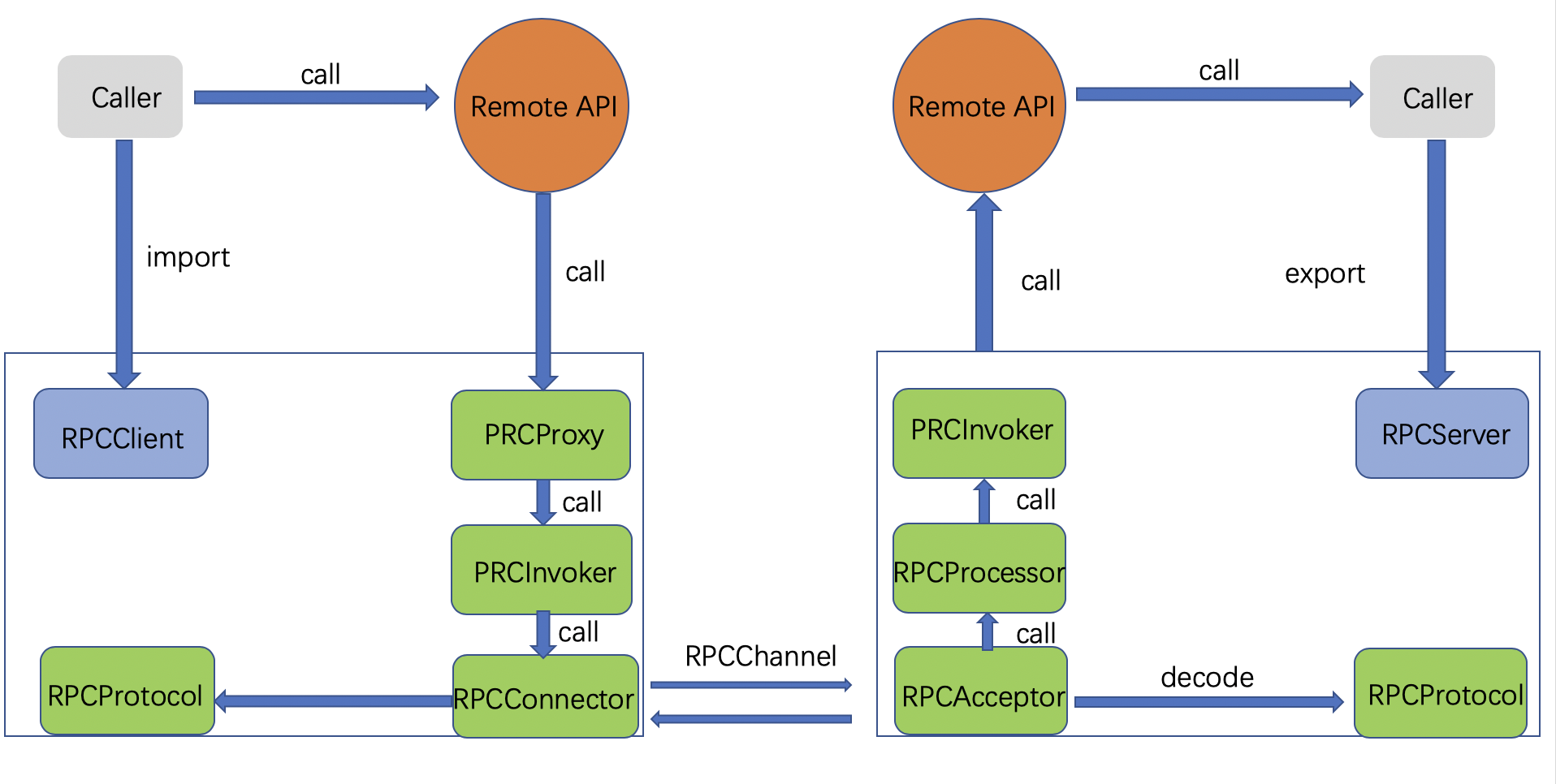
各组件职责:
- RpcServer:负责导出(export)远程接口
- RpcClient:负责导入(import)远程接口的代理实现
- RpcProxy:远程接口的代理实现
- RpcInvoker:
- 客户方实现:负责编码调用信息和发送调用请求到服务方并等待调用结果返回
- 服务方实现:负责调用服务端接口的具体实现并返回调用结果
- RpcProtocol:负责协议编/解码
- RpcConnector:负责维持客户方和服务方的连接通道和发送数据到服务方
- RpcAcceptor:负责接收客户方请求并返回请求结果
- RpcProcessor:负责在服务方控制调用过程,包括管理调用线程池、超时时间等
- RpcChannel:数据传输通道
下面是一段示例代码,以编程的方式创建消费者,并获取RPC接口的Stub:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 |
ApplicationConfig application = new ApplicationConfig(); application.setName( "ITokenVerifyApiStressor" ); RegistryConfig registry = new RegistryConfig(); registry.setAddress( "zookeeper://10.255.223.119:2881" ); ReferenceConfig<ITokenVerifyApi> reference = new ReferenceConfig<ITokenVerifyApi>(); reference.setApplication( application ); reference.setRegistry( registry ); reference.setInterface( ITokenVerifyApi.class ); reference.setVersion( "5.0" ); ITokenVerifyApi api = reference.get(); |
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 |
// 服务的实现 UploadService uploadService = new UpdateServiceImpl(); // Dubbo应用程序信息 ApplicationConfig application = new ApplicationConfig(); application.setName( "UploadServiceProvider" ); // 注册中心配置 RegistryConfig registry = new RegistryConfig(); registry.setAddress( "zookeeper://10.255.223.119:2881" ); // 服务提供者协议配置 ProtocolConfig protocol = new ProtocolConfig(); protocol.setName( "dubbo" ); protocol.setPort( 20880 ); protocol.setThreads( 8 ); protocol.setPayload( 8388608 / 8 / 1024 ); // 暴露服务配置 ServiceConfig<UploadService> service = new ServiceConfig<UploadService>(); service.setApplication( application ); service.setRegistry( registry ); service.setProtocol( protocol ); service.setInterface( UploadService.class ); service.setRef( uploadService ); service.setVersion( "1.0" ); service.export(); |
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 |
<parent> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> <version>2.0.5.RELEASE</version> </parent> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>com.alibaba.spring.boot</groupId> <artifactId>dubbo-spring-boot-starter</artifactId> <version>2.0.0</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.github.sgroschupf</groupId> <artifactId>zkclient</artifactId> <version>0.1</version> </dependency> </dependencies> <build> <plugins> <plugin> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId> </plugin> </plugins> </build> |
|
1 2 3 |
spring.application.name=dubbo-exporter spring.dubbo.server=true spring.dubbo.registry=zookeeper://10.108.94.255:2181 |
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
@SpringBootApplication @EnableDubboConfiguration public class Application { public static void main( String[] args ) { SpringApplication.run( Application.class, args ); } } |
|
1 2 3 4 |
@Service( interfaceClass = MonitorService.class ) @Component public class MonitorServiceImpl implements MonitorService { } |
该注解是 @EnableDubboConfig 和 @DubboComponentScan两者的组合:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 |
@EnableDubboConfig @DubboComponentScan public @interface EnableDubbo { // 扫描 @Service 的基包 @AliasFor(annotation = DubboComponentScan.class, attribute = "basePackages") String[] scanBasePackages() default {}; // 扫描 @Service 的基包(指定的类所在的包) @AliasFor(annotation = DubboComponentScan.class, attribute = "basePackageClasses") Class<?>[] scanBasePackageClasses() default {}; } |
用来配置服务提供方:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 |
package org.apache.dubbo.config.annotation; @Documented @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Target({ElementType.TYPE}) @Inherited public @interface Service { // 实现的 interface 的类 Class<?> interfaceClass() default void.class; // 实现的 interface 的类名 String interfaceName() default ""; // 服务的版本号 String version() default ""; // 服务的分组 String group() default ""; // 是否暴露服务 boolean export() default true; // 是否向注册中心注册服务 boolean register() default true; // 应用程序名称 String application() default ""; // 模块名称 String module() default ""; // 提供者名称 String provider() default ""; // 协议配置 String[] protocol() default {}; // 监控中心配置 String monitor() default ""; // 注册中心配置 String[] registry() default {}; } |
用来配置消费者:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 |
package org.apache.dubbo.config.annotation; @Documented @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Target({ElementType.FIELD, ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE}) public @interface Reference { Class<?> interfaceClass() default void.class; String interfaceName() default ""; String version() default ""; String group() default ""; String url() default ""; String application() default ""; String module() default ""; String consumer() default ""; String protocol() default ""; String monitor() default ""; String[] registry() default {}; } |
Hystrix 旨在通过控制那些访问远程系统、服务和第三方库的节点,从而对延迟和故障提供更强大的容错能力。Hystrix具备拥有回退机制和断路器功能的线程和信号隔离,请求缓存和请求打包,以及监控和配置等功能。
spring boot官方提供了对hystrix的集成,直接在pom.xml里加入依赖:
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-hystrix</artifactId> <version>1.4.4.RELEASE</version> </dependency> |
然后在Application类上增加@EnableHystrix来启用:
|
1 2 3 4 |
@SpringBootApplication @EnableHystrix public class ProviderApplication { } |
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 |
@Service(version = "1.0.0") public class HelloServiceImpl implements HelloService { @HystrixCommand(commandProperties = { @HystrixProperty(name = "circuitBreaker.requestVolumeThreshold", value = "10"), @HystrixProperty(name = "execution.isolation.thread.timeoutInMilliseconds", value = "2000") }) @Override public String sayHello(String name) { throw new RuntimeException("Exception to show hystrix enabled."); } } |
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 |
@Reference(version = "1.0.0") private HelloService demoService; // 降级 @HystrixCommand(fallbackMethod = "reliable") public String doSayHello(String name) { return demoService.sayHello(name); } public String reliable(String name) { return "hystrix fallback value"; } |
新的服务定义/注册机制称为“服务自省”,一个应用只需要注册一条记录,解决了服务推送的性能瓶颈。
Dubbo RPC 协议是构建在 TCP 之上,这有很多优势也有一些缺点,缺点比如通用性、协议穿透性不强,对多语言实现不够友好等。
HTTP/2 由于其标准 HTTP 协议的属性,无疑将具有更好的通用性,现在或将来在各层网络设备上肯定都会得到很好的支持,gRPC 之所以选在 HTTP/2 作为传输层载体很大程度上也是因为这个因素。
Dubbo 支持 gRPC 协议带来的直观好处有:
- 正式支持基于 HTTP/2 的远程通信,在协议通用性和穿透性上进一步提升
- 支持跨进程的 Stream 流式通信,支持 Reactive 风格的 RPC 编程
- 解决了 gRPC 框架难以直接用于微服务开发的问题,将其纳入 Dubbo 的服务治理体系
- 为连接组织内部已有的 gRPC 或多语言体系提供支持
支持 Protobuf 是为了解决Dubbo的跨语言、易用性问题。协议上 2.7.5 版本支持了 gRPC,而关于服务定义与序列化,Protobuf 则提供了很好的解决方案:
- 服务定义:当前 Dubbo 的服务定义和具体的编程语言绑定,没有提供一种语言中立的服务描述格式,比如 Java 就是定义 Interface 接口,到了其他语言又得重新以另外的格式定义一遍。因此 Dubbo 通过支持 Protobuf 实现了语言中立的服务定义
- 序列化。Dubbo 当前支持的序列化包括 Json、Hessian2、Kryo、FST、Java 等,而这其中支持跨语言的只有 Json、Hessian2,通用的 Json 有固有的性能问题,而 Hessian2 无论在效率还是多语言 SDK 方面都有所欠缺。为此,Dubbo 通过支持 Protobuf 序列化来提供更高效、易用的跨语言序列化方案
QPS 性能提升将近 30%、减少了调用过程中的内存分配开销。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 |
ProtocolConfig protocolConfig = new ProtocolConfig("grpc"); protocolConfig.setSslEnabled(true); SslConfig sslConfig = new SslConfig(); sslConfig.setXxxCert(...); DubboBootstrap bootstrap = DubboBootstrap.getInstance(); bootstrap.application(new ApplicationConfig("ssl-provider")) .registry(new RegistryConfig("zookeeper://127.0.0.1:2181")) .protocol(protocolConfig) .ssl(sslConfig); ServiceConfig<GreetingsService> service1 = new ServiceConfig<>(); ServiceConfig<GreetingsService> service2 = new ServiceConfig<>(); bootstrap.service(service1).service(service2); bootstrap.start(); |
在引入 Dubbo Bootstrap 后,新的编程模型变得更简单,并且也为解决了缺少实例级启动入口的问题。
直接支持CompletableFuture。
| 注册中心 | 简化配置模式下,仅仅发布必要的信息到配置中心:
|
||
| 元数据中心 |
包括服务接口名,重试次数,版本号等信息。在2.7之前,元数据存放在注册中心中,导致问题: 推送量大 -> 存储数据量大 -> 网络传输量大 -> 延迟严重 生产者端注册 30+ 参数,有接近一半是不需要传递给注册中心;消费者端注册 25+ 参数,只有个别需要传递给注册中心 2.7仅仅将必要的数据发布到注册中心,全量元数据存放到元数据中心。元数据中心支持Redis、ZooKeeper:
|
||
| 配置中心 |
Spring Cloud Config、Apollo、Nacos 等分布式配置中心组件,都关注以下角度:
Dubbo的2.7 之前的版本中,在 zookeeper 中设置了部分节点:configurators、routers,用于管理部分配置和路由信息,可以看作是Dubbo配置中心的雏形 2.7开始,正式支持配置中心,可以对接到Zookeeper、Apollo、Nacos,配置中心的职责:
|
Dubbo的发展路线是作为服务治理框架,而非简单的RPC框架。在 2.7 中,Dubbo 对其服务治理能力进行了增强,增加了标签路由的能力,并抽象出了应用路由和服务路由的概念。
标签路由可以实现灰度发布。你可以在SPI扩展、过滤器中对请求打标签: RpcContext.getContext().setAttachment(),这样会优先选择匹配的提供者。
泛化调用主要用于消费端没有 API 接口的情况,不需要引入接口 jar 包,而是直接通过 GenericService 接口来发起服务调用,参数及返回值中的所有 POJO 均用 Map 表示。
你需要声明服务引用为泛化的:
|
1 2 |
<dubbo:reference id="userService" interface="com.alibaba.dubbo.samples.generic.api.IUserService" generic="true"/> |
执行泛化调用的代码:
|
1 2 3 4 |
GenericService userService = (GenericService) context.getBean("userService"); // 方法名 参数类型数组 参数值数组 String name = (String) userService.$invoke("delete", new String[]{int.class.getName()}, new Object[]{1}); System.out.println(name); |
从 2.2.0 版本开始,Dubbo 默认在本地以 injvm 的方式暴露服务,在同一个进程里对这个服务的调用会优先走本地调用。
本地调用可以被明确的关闭掉:
|
1 2 3 |
<dubbo:service interface="org.apache.dubbo.samples.local.api.DemoService" ref="target" scope="remote"/> <!-- 显式关闭 --> |
你可以通过URL来明确进行本地调用
|
1 2 |
<dubbo:reference id="demoService" interface="org.apache.dubbo.samples.local.api.DemoService" url="injvm://127.0.0.1/org.apache.dubbo.samples.local.api.DemoService"/> |
在2.6.x及之前的版本提供了一定的异步编程能力,包括Consumer端异步调用、参数回调、事件通知。这些老版本中的异步调用存在缺陷:
- Future获取方式不够直接,需要通过RpcContext获取Future
- Future接口无法实现自动回调,而自定义ResponseFuture虽支持回调但支持的异步场景有限,如不支持Future间的相互协调或组合
- 不支持Provider端异步
2.7.0升级了对Java 8的支持,基于CompletableFuture对当前的异步功能进行了增强,现在服务可以直接返回CompletableFuture:
|
1 2 3 |
public interface AsyncService { CompletableFuture<String> sayHello(String name); } |
如果不想将接口的返回值定义为Future类型,或者存在定义好的同步类型接口,可以重载现有的服务方法:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 |
public interface GreetingsService { String sayHi(String name); // 为了保证方法级服务治理规则依然有效,建议保持方法名不变: sayHi // 使用default实现,避免给服务端提供者带来额外实现成本 // placeholer只是为了实现重载而增加 default CompletableFuture<String> sayHi(String name, boolean placeholer) { return CompletableFuture.completedFuture(sayHello(name)); } } |
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 |
public class AsyncServiceImpl implements AsyncService { public CompletableFuture<String> sayHello(String name) { return CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> { try { Thread.sleep(5000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return "async response from provider."; }); } } |
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 |
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext( new String[]{"META-INF/spring/async-consumer.xml"}); context.start(); final AsyncService asyncService = (AsyncService) context.getBean("asyncService"); CompletableFuture<String> future = asyncService.sayHello("async call request"); future.whenComplete((v, t) -> { if (t != null) { t.printStackTrace(); } else { System.out.println("Response: " + v); } }); System.out.println("Executed before response return."); System.in.read(); } |
采用异步调用后,由于异步结果在异步线程中单独执行,所以流经后半段Filter链的Result是空值,当真正的结果返回时已无法被Filter链处理。为了解决这个问题,2.7.0中为Filter增加了回调接口onResponse:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 |
@Activate(group = {Constants.PROVIDER, Constants.CONSUMER}) public class AsyncPostprocessFilter implements Filter { @Override public Result invoke(Invoker<?> invoker, Invocation invocation) throws RpcException { return invoker.invoke(invoker, invocation); } @Override public Result onResponse(Result result, Invoker<?> invoker, Invocation invocation) { System.out.println("Filter get the return value: " + result.getValue()); return result; } } |
你需要在切换业务线程前自己完成Context的传递:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 |
public class AsyncServiceImpl implements AsyncService { // 保存当前线程的上下文 RpcContext context = RpcContext.getContext(); public CompletableFuture<String> sayHello(String name) { return CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> { // 设置到新线程中 RpcContext.setContext(context); try { Thread.sleep(5000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return "async response from provider."; }); } } |
AsyncContext也提供了signalContextSwitch()的方法来实现方便的Context切换:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 |
public class AsyncServiceImpl implements AsyncService { public String sayHello(String name) { final AsyncContext asyncContext = RpcContext.startAsync(); new Thread(() -> { asyncContext.signalContextSwitch(); try { Thread.sleep(500); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } asyncContext.write("Hello " + name + ", response from provider."); }).start(); return null; } } |
当一个接口有多种实现时,可以用 group 区分:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 |
<!-- 提供者 --> <dubbo:service group="feedback" interface="com.xxx.IndexService" /> <dubbo:service group="member" interface="com.xxx.IndexService" /> <!-- 消费者 --> <dubbo:reference id="feedbackIndexService" group="feedback" interface="com.xxx.IndexService" /> <dubbo:reference id="memberIndexService" group="member" interface="com.xxx.IndexService" /> <!-- 不限制组 --> <dubbo:reference id="barService" interface="com.foo.BarService" group="*" /> |
消费者可以同时调用不同分组中的同一服务,并将结果聚合:
|
1 2 3 |
<dubbo:reference interface="com.xxx.MenuService" group="*" merger="true" /> <dubbo:reference interface="com.xxx.MenuService" group="aaa,bbb" merger="true" /> |
当接口实现出现不兼容升级时,可以用版本号过渡,版本号不同的服务相互间不引用。版本迁移推荐步骤:
- 在低压力时间段,先升级一半提供者为新版本
- 再将所有消费者升级为新版本
- 然后将剩下的一半提供者升级为新版本
如果不需要区分版本,可以这样配置消费者:
|
1 |
<dubbo:reference id="barService" interface="com.foo.BarService" version="*" /> |
报错信息:log4j:WARN No appenders could be found for logger (com.alibaba.dubbo.common.logger.LoggerFactory).
log4j:WARN Please initialize the log4j system properly.
解决方案:添加JVM参数 -Ddubbo.application.logger=slf4j


Leave a Reply